大文件上传和断点续传实例解析
![]() 相关资料:产品首页,
相关资料:产品首页,![]() 白皮书,
白皮书,![]() 控件包,
控件包,![]() 白皮书(图文版),
白皮书(图文版),![]() 产品介绍,
产品介绍,![]() 产品比较,
产品比较,![]() 开发文档,成功案例,基础组件,示例下载,控件包,控件升级,在线演示,在线文档,并发能力,上传速度,下载速度,
开发文档,成功案例,基础组件,示例下载,控件包,控件升级,在线演示,在线文档,并发能力,上传速度,下载速度,![]() Windows控件安装,
Windows控件安装,![]() macOS控件安装,
macOS控件安装,![]() Linux-deb控件安装,
Linux-deb控件安装,![]() Linux-rpm控件安装,安装引导,控件布署,控件升级,
Linux-rpm控件安装,安装引导,控件布署,控件升级,![]() IE9加载控件,
IE9加载控件,![]() IE8加载控件,
IE8加载控件,
标杆案例:![]() 中国港湾,
中国港湾,![]() 中国中车,
中国中车,![]() 中国石油,
中国石油,![]() 中国石化,
中国石化,![]() 长江电力,
长江电力,![]() 中信证券,
中信证券,![]() 上海通用,
上海通用,![]() 一汽大众,沈阳自动化研究所,
一汽大众,沈阳自动化研究所,
![]() 解决方案:
解决方案:![]() 党政,
党政,![]() 央企,
央企,![]() 国防军工,
国防军工,![]() 房地产,
房地产,![]() 档案管理,
档案管理,![]() 教育,
教育,![]() 医疗,
医疗,![]() 工程管理,
工程管理,![]() 企业文件传输解决方案,
企业文件传输解决方案,
![]() 示例下载:
示例下载:![]() asp.net-vs2013,
asp.net-vs2013,![]() asp.net-vs2010,
asp.net-vs2010,![]() jsp-eclipse,
jsp-eclipse,![]() jsp-springboot,
jsp-springboot,![]() jsp-myeclipse,
jsp-myeclipse,![]() php,
php,![]() vue-cil,
vue-cil,![]() WinForm(C#),
WinForm(C#),![]() C++(WTL)
C++(WTL)
![]() 教程:
教程:![]() WinForm(C#)测试,
WinForm(C#)测试,![]() WTL(C++)测试,在vue.js中使用,在vue-cli中使用,eclipse导入up6
WTL(C++)测试,在vue.js中使用,在vue-cli中使用,eclipse导入up6
![]() 视频教程:
视频教程:![]() windows控件安装,
windows控件安装,![]() mac控件安装,
mac控件安装,![]() linux-deb控件包安装,
linux-deb控件包安装,![]() linux-rpm控件包安装,
linux-rpm控件包安装,![]() php7测试,
php7测试,![]() php5测试,
php5测试,![]() vue-cli-测试,asp.net-IIS Express测试,asp.net-IIS测试,
vue-cli-测试,asp.net-IIS Express测试,asp.net-IIS测试,![]() asp.net-阿里云(oss)测试,
asp.net-阿里云(oss)测试,![]() asp.net-华为云(obs)测试,
asp.net-华为云(obs)测试,![]() jsp-springboot测试,
jsp-springboot测试,![]() ActiveX(x86)源码编译,
ActiveX(x86)源码编译,![]() ActiveX(x64)源码编译,
ActiveX(x64)源码编译,![]() Windows(npapi)源码编译,
Windows(npapi)源码编译,![]() macOS源码编译,
macOS源码编译,![]() Linux(x86_64)源码编译,
Linux(x86_64)源码编译,![]() Linux(arm)源码编译,
Linux(arm)源码编译,![]() Linux(mips-uos)源码编译,
Linux(mips-uos)源码编译,![]() Linux(mips-kylin-涉密环境)源码编译,sm4加密传输,压缩传输,
Linux(mips-kylin-涉密环境)源码编译,sm4加密传输,压缩传输,![]() jsp-eclipse-sm4加密存储,
jsp-eclipse-sm4加密存储,![]() jsp-springboot-sm4加密存储,
jsp-springboot-sm4加密存储,![]() asp.net-sm4加密存储
asp.net-sm4加密存储
![]() ASP.NET教程:asp.net,IIS Express,IIS,IIS-Https,
ASP.NET教程:asp.net,IIS Express,IIS,IIS-Https,![]() Oracle,minio,fastdfs,
Oracle,minio,fastdfs,![]() 阿里云对象存储(oss),
阿里云对象存储(oss),![]() 华为云对象存储(obs)
华为云对象存储(obs)
![]() jsp-eclipse教程:测试教程,
jsp-eclipse教程:测试教程,![]() oracle,
oracle,![]() mysql,
mysql,![]() SQL Server,minio,fastdfs,
SQL Server,minio,fastdfs,![]() 阿里云对象存储(oss),
阿里云对象存储(oss),![]() 华为云对象存储(obs),
华为云对象存储(obs),
![]() jsp-springboot教程:测试教程,minio,fastdfs,
jsp-springboot教程:测试教程,minio,fastdfs,![]() 阿里云对象存储(oss),
阿里云对象存储(oss),![]() 华为云对象存储(obs)
华为云对象存储(obs)
![]() jsp-myeclipse教程:
jsp-myeclipse教程:![]() mysql,oracle,
mysql,oracle,![]() SQL Server,fastdfs
SQL Server,fastdfs
![]() php教程:测试教程,minio,fastdfs,
php教程:测试教程,minio,fastdfs,![]() 阿里云对象存储(oss),
阿里云对象存储(oss),
![]() 二次开发:组件引用,自定义事件,自定义业务字段,自定义文件保存路径,授权码,加密存储,加密传输,使用Minio存储,使用FastDFS存储,
二次开发:组件引用,自定义事件,自定义业务字段,自定义文件保存路径,授权码,加密存储,加密传输,使用Minio存储,使用FastDFS存储,![]() 使用达梦数据库,数据表字段设计,监控fd_create流程,监控f_create流程,监控f_list.jsp流程
使用达梦数据库,数据表字段设计,监控fd_create流程,监控f_create流程,监控f_list.jsp流程
![]() 相关问题:WebSocket连接失败,md5计算完毕后卡住,域名未授权,网站安全系统拦截,
相关问题:WebSocket连接失败,md5计算完毕后卡住,域名未授权,网站安全系统拦截,
![]() 联系我们:
联系我们:![]() QQ:1269085759(技术),
QQ:1269085759(技术),![]() QQ:3040217208(售后),
QQ:3040217208(售后),![]() QQ:1085617561(商务),
QQ:1085617561(商务),![]() 微信:13235643658,
微信:13235643658,![]() 邮箱:1269085759@qq.com,
邮箱:1269085759@qq.com,![]() 1085617561@qq.com,
1085617561@qq.com,![]() qwl@ncmem.com,
qwl@ncmem.com,








视频教程:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1jm4y127Ut/?vd_source=d1843c7f8c164416779b5188178bad8c
1.下载示例
https://gitee.com/xproer/up6-vue-cli
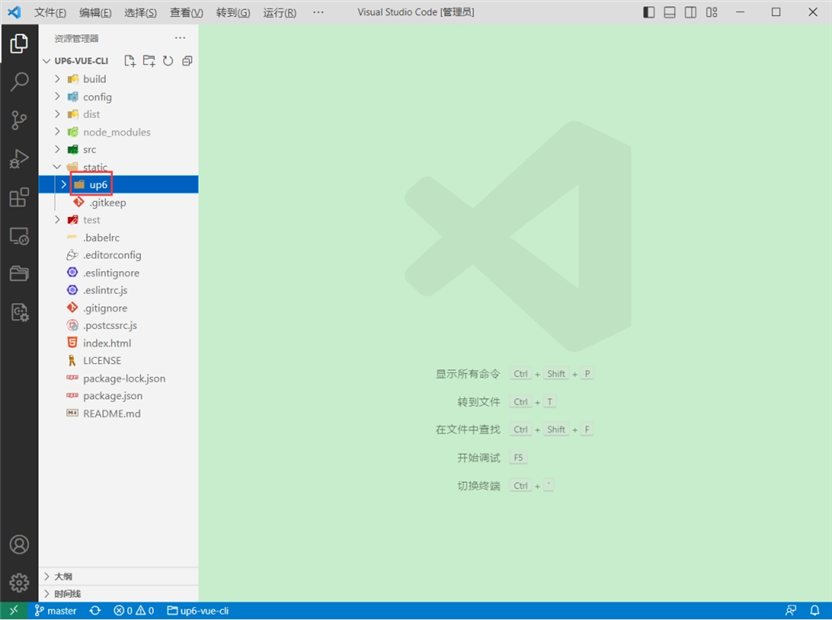
将up6组件复制到项目中
示例中已经包含此目录
1.引入up6组件
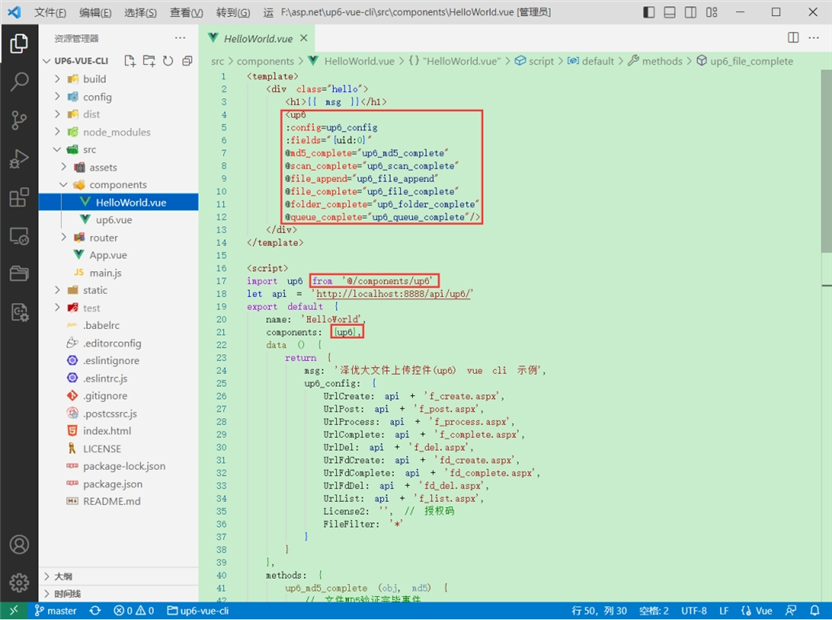
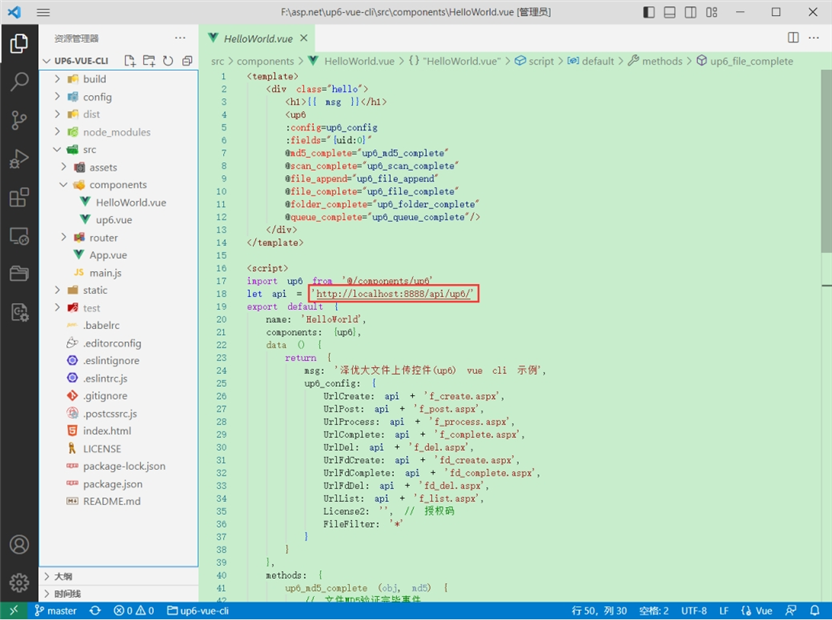
2.配置接口地址
接口地址分别对应:文件初始化,文件数据上传,文件进度,文件上传完毕,文件删除,文件夹初始化,文件夹删除,文件列表
参考:http://www.ncmem.com/doc/view.aspx?id=e1f49f3e1d4742e19135e00bd41fa3de
3.处理事件
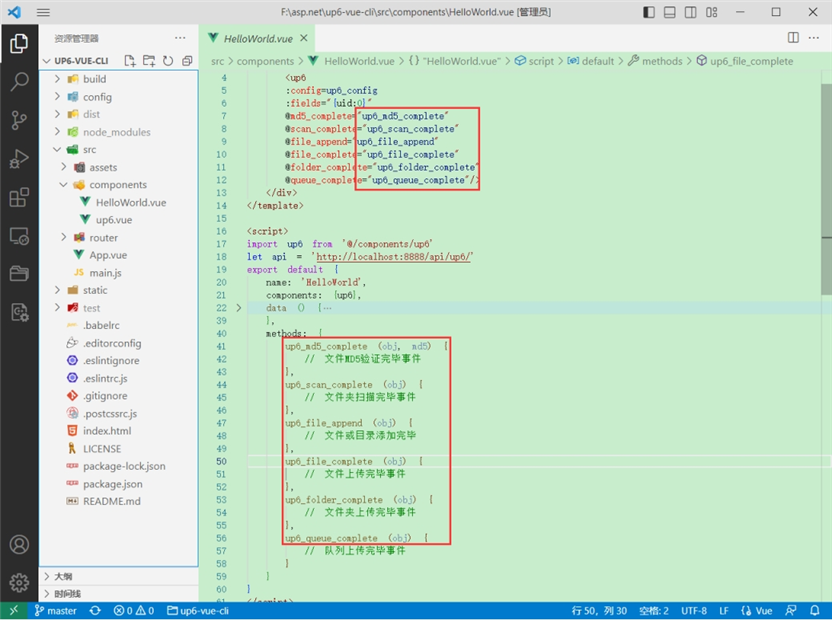
启动测试
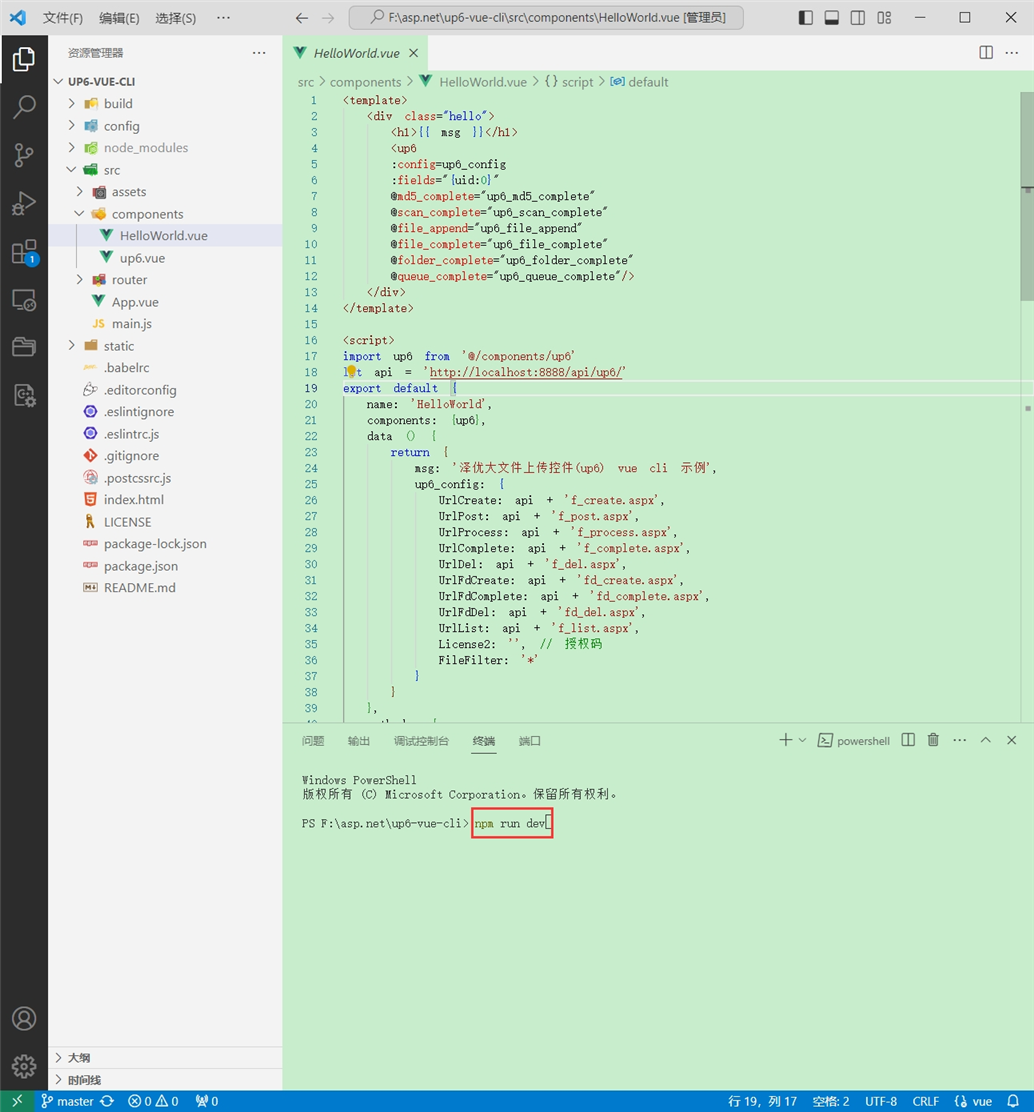
启动成功
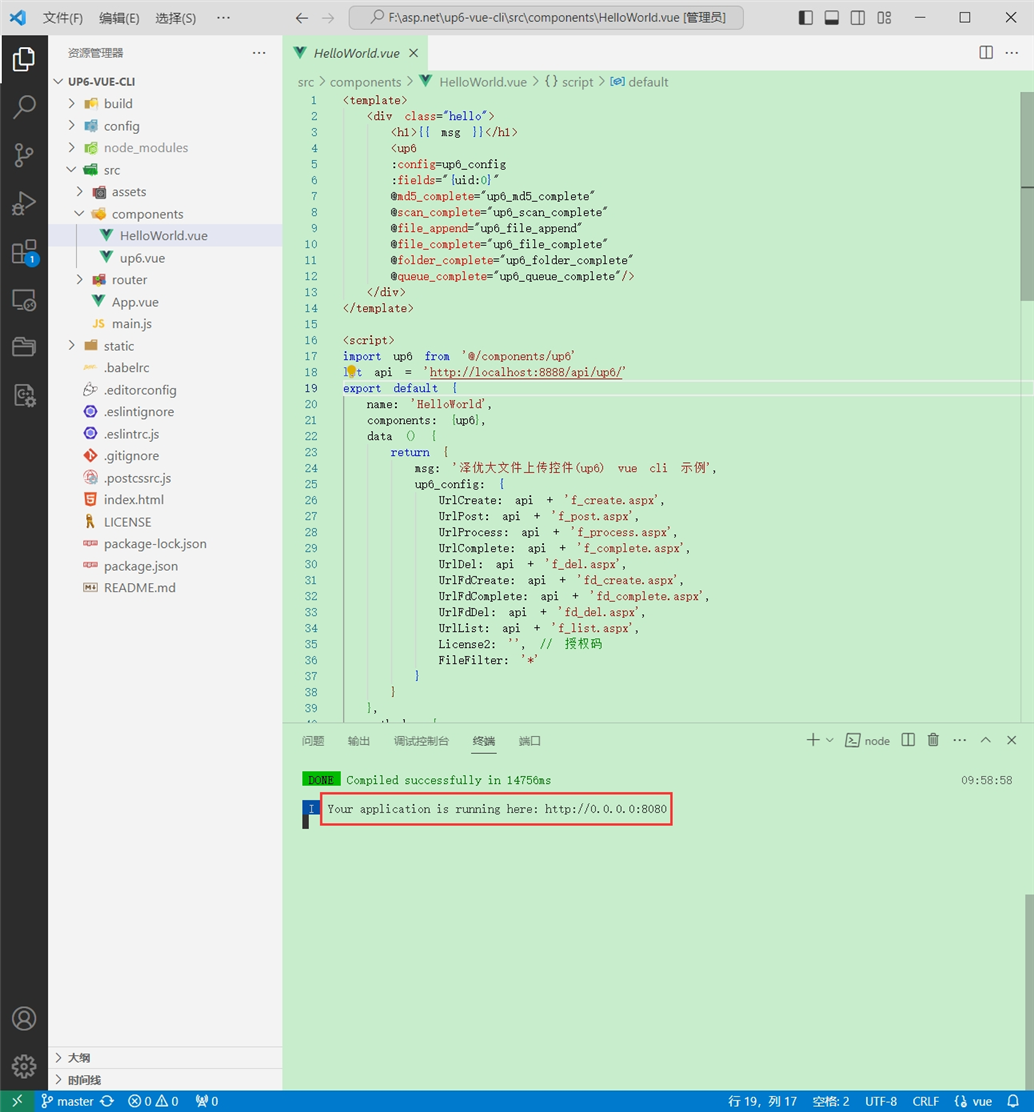
效果
数据库
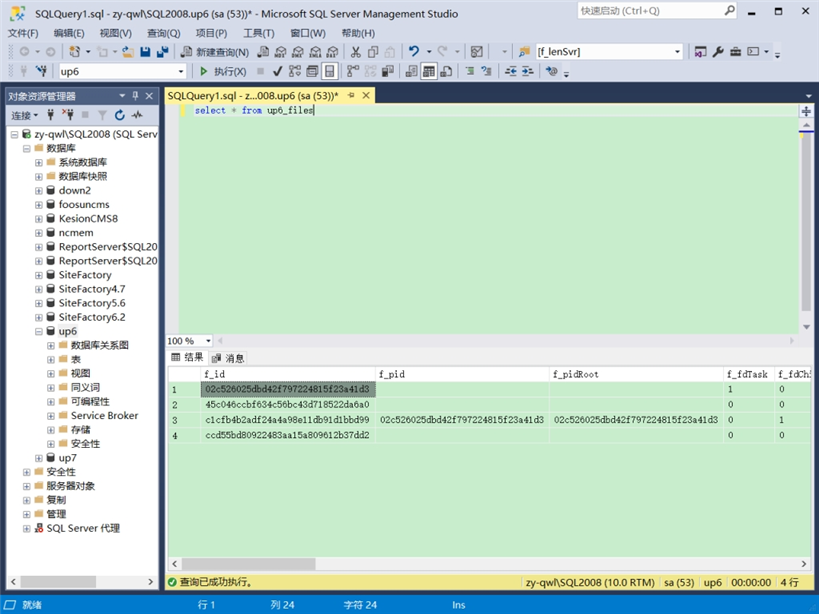
大文件上传控件(up6)
个人版:http://www.ncmem.com/webapp/up6/purchase.aspx
源码工程文档:https://drive.weixin.qq.com/s?k=ACoAYgezAAw1dWofra
